If you read my T-SQL Tuesday post from this month, I mentioned that I’ve been using Azure Data Studio on daily basis. One of the things that I find I use it for the most is for Source Control with Git. I’m incredibly surprised by this. Maybe it comes from years of using Management Studio and not being able to check in code from the tool that I’m using to write it. (Or maybe I’ve been able to do that all this time and no one told me…?)
- Microsoft Azure File Explorer Download
- File Explorer Azure Web App
- File Explorer Azure
- Azure Storage Explorer Download 64 Bit
- File Explorer Azure Certification
You need to enable JavaScript to run this app. Azure Data Explorer. You need to enable JavaScript to run this app. It is really simple to use the Kudu Service to view, edit, add, and remove files from your Web App. But as you can see there are a lot of capabilities that Kudu brings to Azure Web apps. Another really useful ability that Kudu gives you is the ability to view log files.
Microsoft Azure File Explorer Download
As I’m using it, I found two things that have helped me out. So naturally, I thought I’d share.
Multiple Repos
The most useful piece of functionality that I’m taking advantage of right now is working with multiple repos at the same time from within Azure Data Studio.

What I had been doing is opening the single repo folder when in Azure Data Studio. (File -> Open Folder -> GitRepoSQL_Presentations) Here you can see that I’m in the repo, by looking at the title bar of ADS.
But I’ve also created a repository for scripts that I’m using in blog posts. If I want to make changes there using this setup, I would then have to open that folder. This means that I would have to close any open file that I have. So if I was in the middle of working on a script for SQL Presentations, I would have to stop what I’m doing, save and close the file, so I could do a change for the other repo.
That’s a bit of pain if you are constantly working from multiple repos. But you don’t have to do that.
I have set up my directories so that all of my repos are in the same folder, GitRepo. If I open the parent directory, GitRepo, ADS will recognize that I have 2 repositories:
From here, I can still do the various Git actions I need to do for each repo without disrupting any other work I have for other projects. The other nice thing is that I can easily see what branch I’m in by looking to the right of the folder name. The asterisk by the branch name means that there are changes locally.
Explorer
Another area of Azure Data Studio I’ve been using more is the Explorer. This is where you can get a list of all the open windows as well as all of the files in the folder you have open. If you create a new file and you realize you need to rename it, you can do that here. You can open files for editing as well as see if there are files that have been checked and have been modified or added. For the record, I haven’t yet tested deleting or renaming a file that’s been checked in. I know Git is pretty specific about how you do those actions but since I can have ADS open File Explorer, I can just jump there and use TortoiseGit to make those changes and go back to ADS for check-in.
Since the Explorer shows you all files, and not just those that have been added to source control, you can work with those files and then switch to Source Control to check those in. Now that I see what’s there, it’s been pretty a useful tool as I’m working with files. And because it uses the same directory as the folder that I’ve opened, I can again use this for all the files across the multiple repos as needed.
These are just two small details with ADS that I found pretty useful to my productivity so I thought I’d share them with you in the hopes that they help you too. Sometimes it’s the little things that make a big difference.
-->Overview
Azure Blob Storage is a service for storing large amounts of unstructured data, such as text or binary data, that can be accessed from anywhere in the world via HTTP or HTTPS.You can use Blob storage to expose data publicly to the world, or to store application data privately. In this article, you'll learn how to use Storage Explorerto work with blob containers and blobs.
Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this article, you'll need the following:
Create a blob container
All blobs must reside in a blob container, which is simply a logical grouping of blobs. An account can contain an unlimited number of containers, and each container can store an unlimited number of blobs.
The following steps illustrate how to create a blob container within Storage Explorer. Sougou for mac.
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account within which you wish to create the blob container.
Right-click Blob Containers, and - from the context menu - select Create Blob Container.
A text box will appear below the Blob Containers folder. Enter the name for your blob container. See Create a container for information on rules and restrictions on naming blob containers.
Press Enter when done to create the blob container, or Esc to cancel. Once the blob container has been successfully created, it will be displayed under the Blob Containers folder for the selected storage account.
View a blob container's contents
Blob containers contain blobs and folders (that can also contain blobs).
The following steps illustrate how to view the contents of a blob container within Storage Explorer:
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to view.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the blob container you wish to view, and - from the context menu - select Open Blob Container Editor.You can also double-click the blob container you wish to view.
The main pane will display the blob container's contents.
Delete a blob container
Blob containers can be easily created and deleted as needed. (To see how to delete individual blobs,refer to the section, Managing blobs in a blob container.)
The following steps illustrate how to delete a blob container within Storage Explorer:
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to view.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the blob container you wish to delete, and - from the context menu - select Delete.You can also press Delete to delete the currently selected blob container.
Select Yes to the confirmation dialog.

Copy a blob container
Storage Explorer enables you to copy a blob container to the clipboard, and then paste that blob container into another storage account. (To see how to copy individual blobs,refer to the section, Managing blobs in a blob container.)
The following steps illustrate how to copy a blob container from one storage account to another.
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to copy.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the blob container you wish to copy, and - from the context menu - select Copy Blob Container.
Right-click the desired 'target' storage account into which you want to paste the blob container, and - from the context menu - select Paste Blob Container.
Get the SAS for a blob container
A shared access signature (SAS) provides delegated access to resources in your storage account.This means that you can grant a client limited permissions to objects in your storage account for a specified period of time and with a specified set of permissions, without having toshare your account access keys.
The following steps illustrate how to create a SAS for a blob container:
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container for which you wish to get a SAS.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Right-click the desired blob container, and - from the context menu - select Get Shared Access Signature.
In the Shared Access Signature dialog, specify the policy, start and expiration dates, time zone, and access levels you want for the resource.
When you're finished specifying the SAS options, select Create.
A second Shared Access Signature dialog will then display that lists the blob container along with the URL and QueryStrings you can use to access the storage resource.Select Copy next to the URL you wish to copy to the clipboard.
When done, select Close.
Manage Access Policies for a blob container
The following steps illustrate how to manage (add and remove) access policies for a blob container:
Open Storage Explorer.
Tyga twitter. In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container whose access policies you wish to manage.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Select the desired blob container, and - from the context menu - select Manage Access Policies.
The Access Policies dialog will list any access policies already created for the selected blob container.
Follow these steps depending on the access policy management task:
- Add a new access policy - Select Add. Once generated, the Access Policies dialog will display the newly added access policy (with default settings).
- Edit an access policy - Make any desired edits, and select Save.
- Remove an access policy - Select Remove next to the access policy you wish to remove.
Set the Public Access Level for a blob container
File Explorer Azure Web App
By default, every blob container is set to 'No public access'.
The following steps illustrate how to specify a public access level for a blob container.
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container whose access policies you wish to manage.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Select the desired blob container, and - from the context menu - select Set Public Access Level.
In the Set Container Public Access Level Download digital keyboard for laptop. dialog, specify the desired access level.
Select Apply.
File Explorer Azure
Managing blobs in a blob container
Once you've created a blob container, you can upload a blob to that blob container, download a blob to your local computer, open a blob on your local computer,and much more.
Azure Storage Explorer Download 64 Bit
The following steps illustrate how to manage the blobs (and folders) within a blob container.
Open Storage Explorer.
In the left pane, expand the storage account containing the blob container you wish to manage.
Expand the storage account's Blob Containers.
Double-click the blob container you wish to view.
The main pane will display the blob container's contents.
The main pane will display the blob container's contents.
Follow these steps depending on the task you wish to perform:
Upload files to a blob container
On the main pane's toolbar, select Upload, and then Upload Files from the drop-down menu.
In the Upload files dialog, select the ellipsis (…) button on the right side of the Files text box to select the file(s) you wish to upload.
Specify the type of Blob type. See Create a container for more information.
Optionally, specify a target folder into which the selected file(s) will be uploaded. If the target folder doesn’t exist, it will be created.
Select Upload.
Upload a folder to a blob container
On the main pane's toolbar, select Upload, and then Upload Folder from the drop-down menu.
In the Upload folder dialog, select the ellipsis (…) button on the right side of the Folder text box to select the folder whose contents you wish to upload.
Specify the type of Blob type. See Create a container for more information.
Optionally, specify a target folder into which the selected folder's contents will be uploaded. If the target folder doesn’t exist, it will be created.
Select Upload.
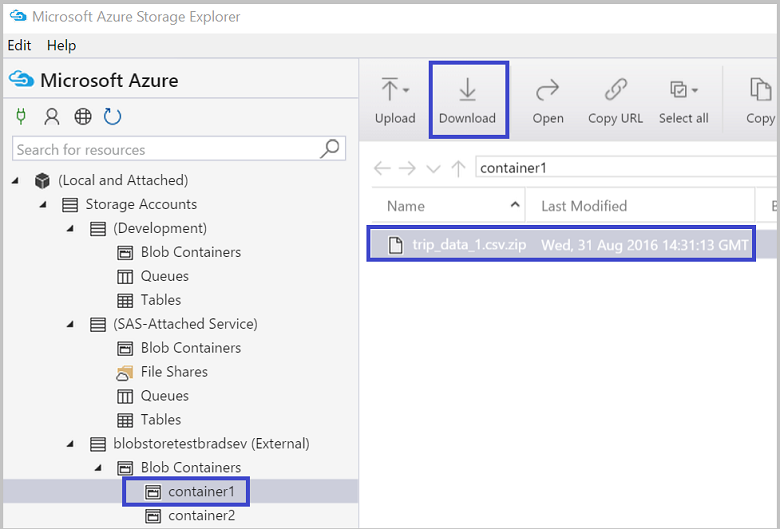
Download a blob to your local computer
- Select the blob you wish to download.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Download.
- In the Specify where to save the downloaded blob dialog, specify the location where you want the blob downloaded, and the name you wish to give it.
- Select Save.
Open a blob on your local computer
- Select the blob you wish to open.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Open.
- The blob will be downloaded and opened using the application associated with the blob's underlying file type.
Copy a blob to the clipboard
- Select the blob you wish to copy.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Copy.
- In the left pane, navigate to another blob container, and double-click it to view it in the main pane.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Paste to create a copy of the blob.
Delete a blob
- Select the blob you wish to delete.
- On the main pane's toolbar, select Delete.
- Select Yes to the confirmation dialog.
File Explorer Azure Certification
Next steps
- View the latest Storage Explorer release notes and videos.
- Learn how to create applications using Azure blobs, tables, queues, and files.
